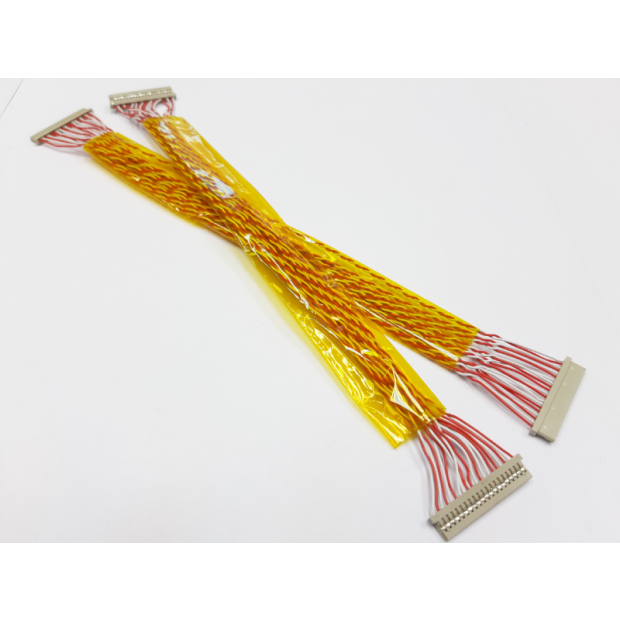
LVDS
Low-Voltage Differential Signaling (LVDS) is an electronic signal system that can meet today's demand for high-performance data transmission applications. At the same time, the system power supply voltage is reduced to 2 volts, which is suitable for TFT LCDs with higher resolution than SVGA. Display devices have been widely used at present, and can even be embedded in FPGA, ASIC or other components.
Like USB and 1394, LVDS is a differential signal. In November 1995, the ANSI/TIA/EIA-644 plan "Electrical Characteristics of Low Voltage Differential Signaling (LVDS) Interface Circuits." was certified. Introduced by National Semiconductor Corporation in 1994. LVDS uses a differential transmission method, and the voltage output and the receiving end require a terminating resistor (Terminating Resistor) of 100 ohms. LVDS allows point-to-point (Point-to-Point) and branch (Multi-Drop) connections. Use MS (Microstrip) lines or ST (Stripline) lines to realize differential signals.
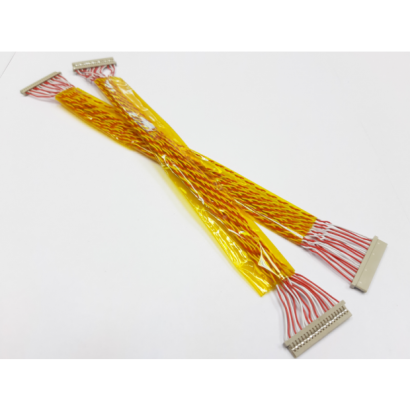 LVDS
LVDS